Intents and Entities – The Building Blocks of an AI Chatbot
Intents and Entities – The Building Blocks of an AI Chatbot
Intents and entities evidently help AI identify the motive behind a user’s question. The fundamental task of any chatbot is to analyse and observe a user’s intent and develop solutions that cater to their needs.
The AI technology that fuels the effectiveness of chatbots is Natural Language Processing (NLP). It helps machines understand human language and vice versa. But before delving deeper into this, let’s understand the equation and the variables behind the functionality of a chatbot.
- Utterance:
An utterance is a query, or a sentence typed in by a user. These are often complete sentences or meaningful phrases.
- Intent:
Intent refers to a user’s goal behind a command or a query. It denotes the intention behind a user’s “utterance.”
- Entity:
An entity can act as a modifier. It is referred to as the data user shares to describe their “intent.” It provides more context for the machine to resolve the query.
Let’s try to understand these terms better with the help of an example:
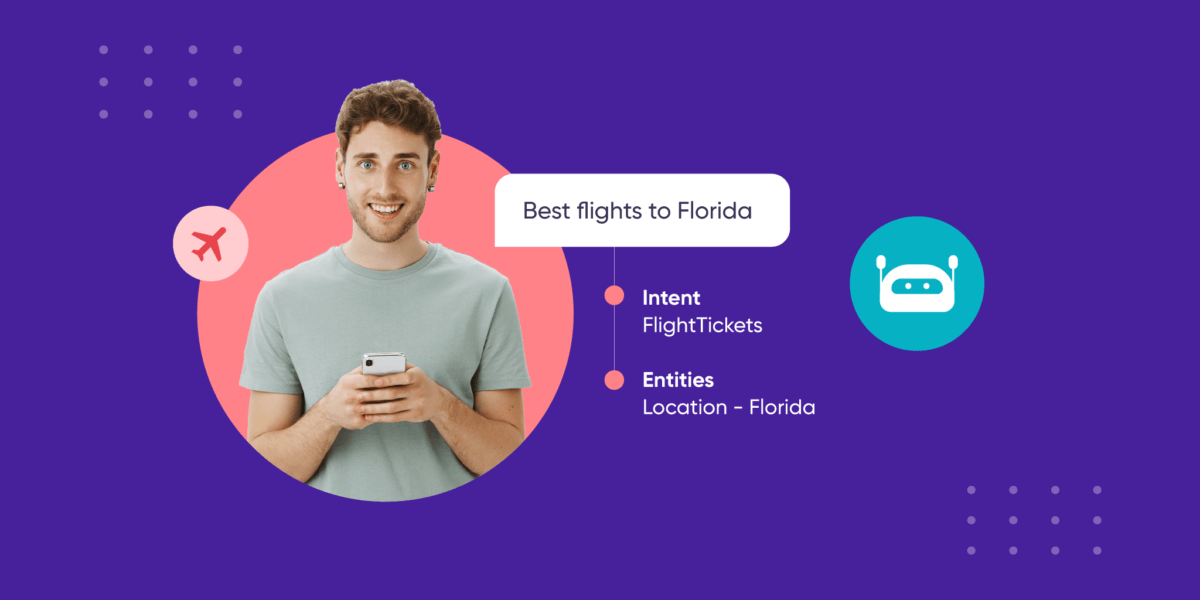
“Show me the fastest way to Cubbon Park.”
Here, the utterance is the complete phrase. The intent here can be “get Directions,” and the entity will be “fastest” and “Cubbon Park” as they provide context to the user intent.
In a nutshell, intents and entities give directions to Chatbots and enable them to meet customers’ needs in the best way possible. But to better understand how exactly intents and entities make chatbots functional, let’s dive into certain concepts more deeply.
Table of Contents
- What is intent in a chatbot?
- What is an entity in a chatbot?
- Are there different types of entities in NLP?
- How are intents and entities different?
- What are some examples of chatbot intents & entities in different industries?
What is intent in a chatbot?
Intent refers to a user’s purpose behind a command put up in a digital space. It extracts the meaning behind a user’s “utterance.” It is a means to an end, carried out by the user with the expectation of an apt solution. The efficiency of any chatbot is undeniably determined by how well it can identify the user’s needs, i.e., their intent, and efficiently solve their problems. If the machine knows the intent accurately, it is easy to serve users with the correct answers and action prompts.
This heavy lifting is carried out using complex Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence algorithms, and the process is known as Intent Classification.
Intents are classified into distinct categories, but to train a chatbot to identify and acknowledge them. Chatbot Intent Datasets are used to get them accustomed to such categories. We talk in detail about these two crucial elements of chatbots below!
Chatbot Intent Classification:
This is a complex process where the machine takes the user’s utterances and classifies them into pre-defined buckets. The system takes the help of NLP models, which have evolved over the years to understand languages humans use and then categorise them into different buckets. The developer determines these buckets or functions carefully. Later, he processes an action or a result to be served to the user accordingly.
Chatbot Intent Dataset:
Intent Classification is an essential task for any chatbot. One of the biggest challenges during this process is customising it for your specific business logic, which is solved using intent datasets. This dataset trains your system to identify users’ queries’ intent correctly. These datasets often define intents, how to identify those intents, entities that modify intents, and the action to be taken for this intent specific to your industry and use cases.
You can read more about user intents in artificial intelligence here.
What is an entity in a chatbot?
Entities distinguish intents into elaborate categories and provide results according to the respective type. They are considered the secondary tool that certainly maintains the streak of accuracy in a chatbot. Entities extract and analyse the meaning behind an utterance from intents and personalise the user experience by providing the most relevant results.
Suppose a user types “garages near me.” The user intent is to find garages and such garages that are nearby. Entities are “garage” and “user’s location”, which helps you give more context to the user’s intent. Then it provides the results of all the garages closest to the user.
An accurate prediction from an entity essentially solves a user’s query!
Different types of entities in NLP
Entities are pre-dominantly divided in two categories within Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- System defined entities
System defined entities are readily available entities that are pre-built within the system. A few examples of such entities can be a user’s current date, current time, location, email addresses, phone numbers, URLs and more!
- Custom entities
Custom entities are not well-established within the system. They are narrowed down to the specifics to match users’ needs and preferences. Examples of such entities are a user’s transaction history, a cab ride, a travel ticket, a shopping query, and more!
These different entities can take over following the intent and accurately delivering results.
How are intents and entities different?
There is a fundamental difference between intents and entities. The intent is the action initiated by the user or a goal they have in mind, conversely, the entity is what refines, modifies and gives more context to the said action or intent. Intent can be arbitrary and refer to many things, but entities can be condensed to texts, data or fields.
Through Natural Language Processing, intents and entities in chatbots co-exist and make AI chatbots reliable and user-friendly.
For example, if the user query is “what is the temperature today in Amsterdam?” The user intent is to find out the weather conditions in Amsterdam, and the entity becomes “temperature” “today” and “Amsterdam.” after extracting the same from the user utterance.
Similarly, if the user intent is “what is the score for today’s football match?”, the entity is “score”, “today”, and “football match.” This information is extracted from user utterances!
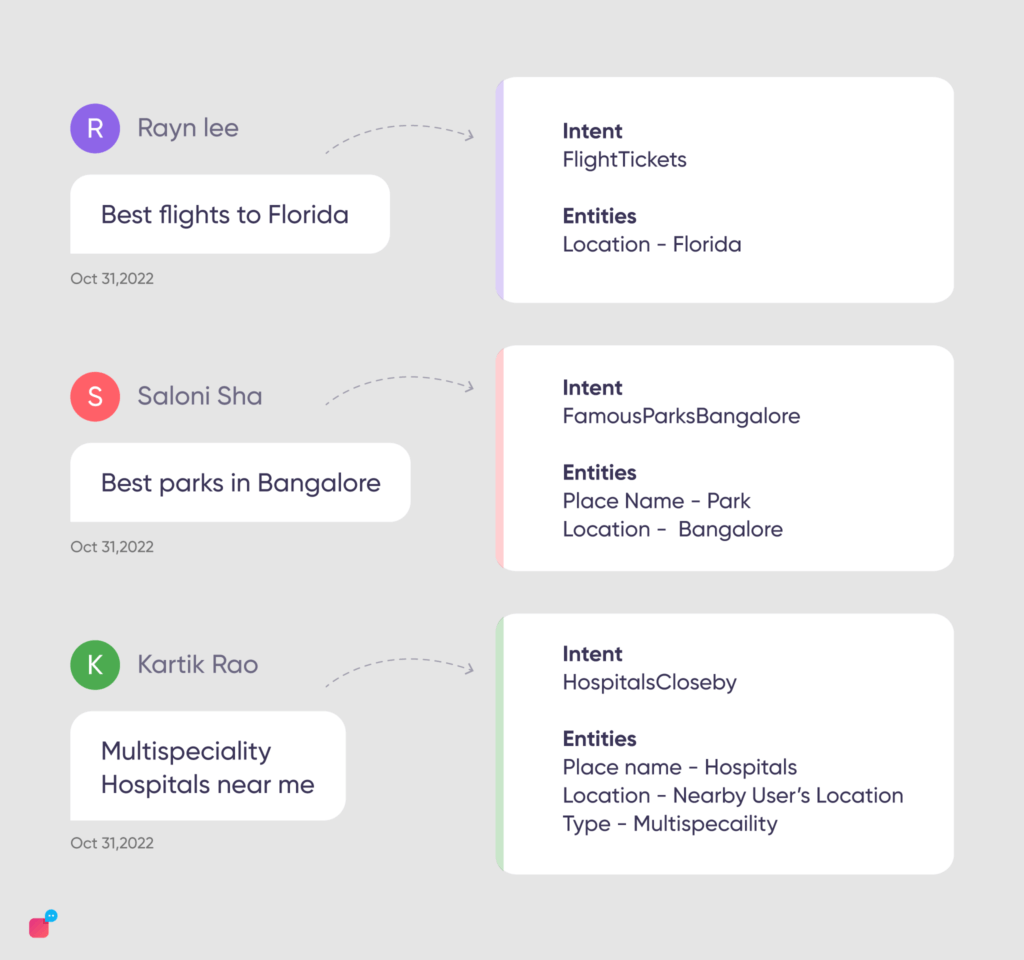
Examples of chatbot intents & entities in different industries
1. Delivery apps and services:
An average person in most urban cities uses delivery apps almost daily to meet all of their needs. Moreover, this trend is rising exponentially as these companies expand their services. Companies use chatbots for customer service and satisfaction to keep up with these rising demands. They try to collect the preliminary data and do an initial triaging of the problem using chatbots before letting human agents take over.
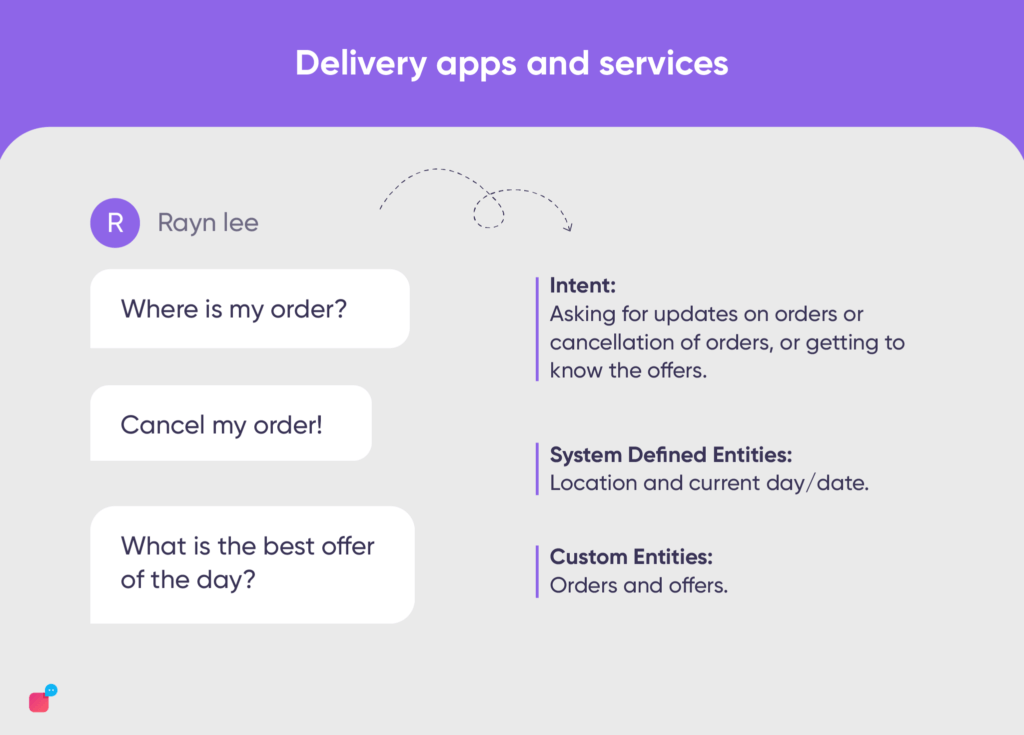
Some of the examples of queries asked by customers can be:
“Where is my order?”, “Cancel my order!”, “What is the best offer of the day?”
In the above user utterances, we can finally identify,
- Intent: Asking for updates on orders or cancellation of orders, or getting to know the offers.
- System Defined Entities: Location and current day/date.
- Custom Entities: Orders and offers.
2. E-commerce sites and platforms
Like delivery apps, E-commerce platforms certainly have evolved the concept of users interacting with a business and products. On a day-to-day basis, users reach out to specific E-commerce platforms to meet their needs at a reasonable cost! They also prioritise timely deliveries and durable products delivered to their doorsteps. In such a case, E-commerce sites utilise conversational AI and chatbots to resolve a bulk of customer service queries.
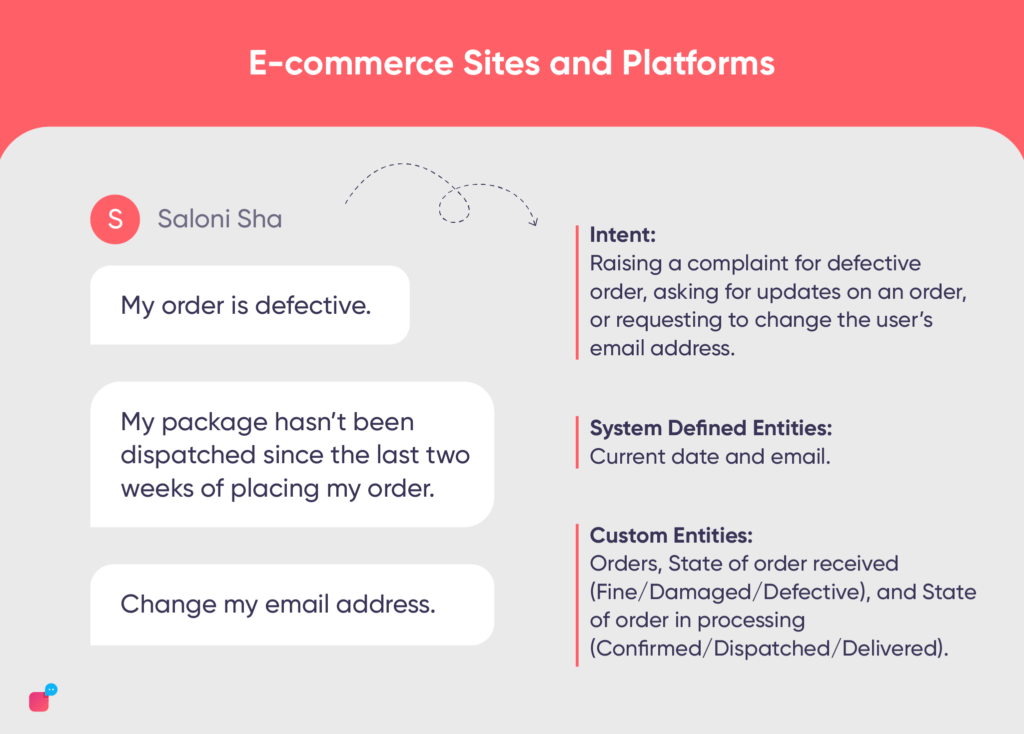
Some examples of chatbot intents and utterances initiated by customers can be:
“My order is defective.”, “My package hasn’t been dispatched since the last two weeks of placing my order.”, “Change my email address.”
In the above user utterances, we can finally identify
- Intent: Raising a complaint for defective order, asking for updates on an order, or requesting to change the user’s email address.
- System Defined Entities: Current date and email.
- Custom Entities: Orders, State of order received (Fine/Damaged/Defective), and State of order in processing (Confirmed/Dispatched/Delivered).
3. Online banking sites
Gone are the days when people stand in long queues specifically to fulfil their banking duties. Nowadays, banking transactions are incredibly safe, secure and less time-consuming, and the credit goes to banking sites that have welcomed automation to improve their processes.
They rely on Conversational AI and Chatbots to carry out numerous transactions with customers. They can be as small as paying bills, whereas checking the account balance or bank statements, resetting banking passwords, or as big as opening a new bank account and initiating fund transfers between accounts.
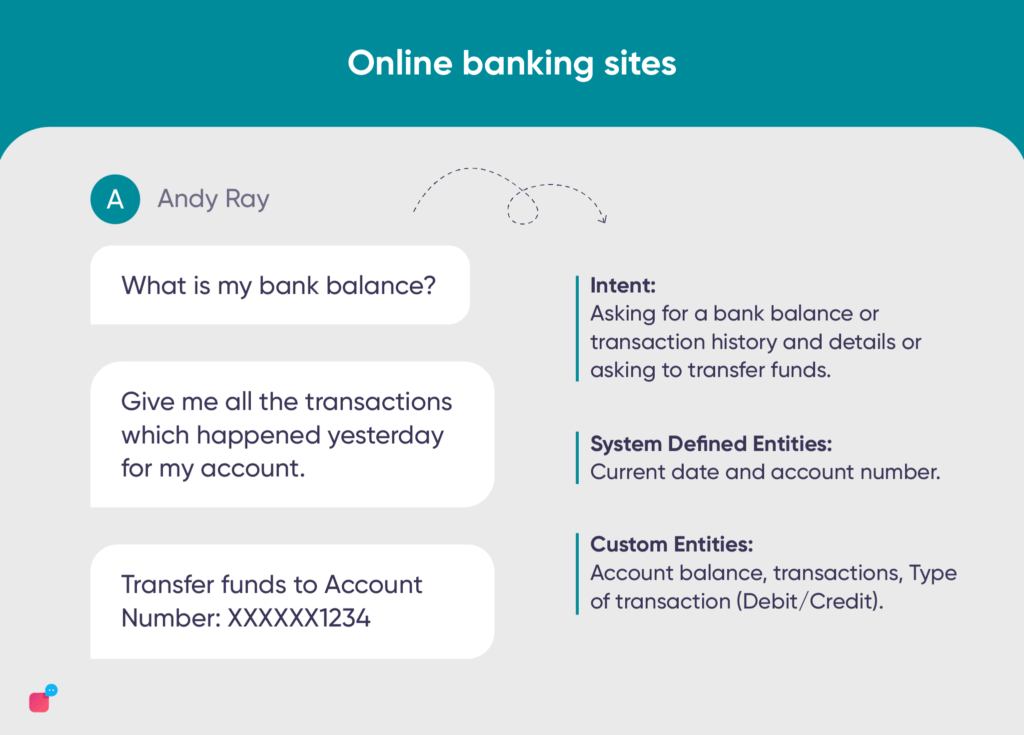
Some examples of chatbot intents and utterances initiated by customers can be:
“What is my bank balance?”, “Give me all the transactions which happened yesterday for my account.”, “Transfer funds to Account Number: XXXXXX1234”
In the above user utterances, we can finally identify
- Intent: Asking for a bank balance or transaction history and details or asking to transfer funds.
- System Defined Entities: Current date and account number.
- Custom Entities: Account balance, transactions, type of transaction (Debit/Credit).
4. Travel websites
A study by Sprinklr shows that customers prefer interacting with chatbots on a travel website because of their friendliness, reliability and responsiveness.
Some of a customer’s basic needs from a travel website are answering their queries at any given time, laying down recommendations per their preferences and budget, answering FAQs in a matter of seconds, and helping them narrow down their search as per their requirements.
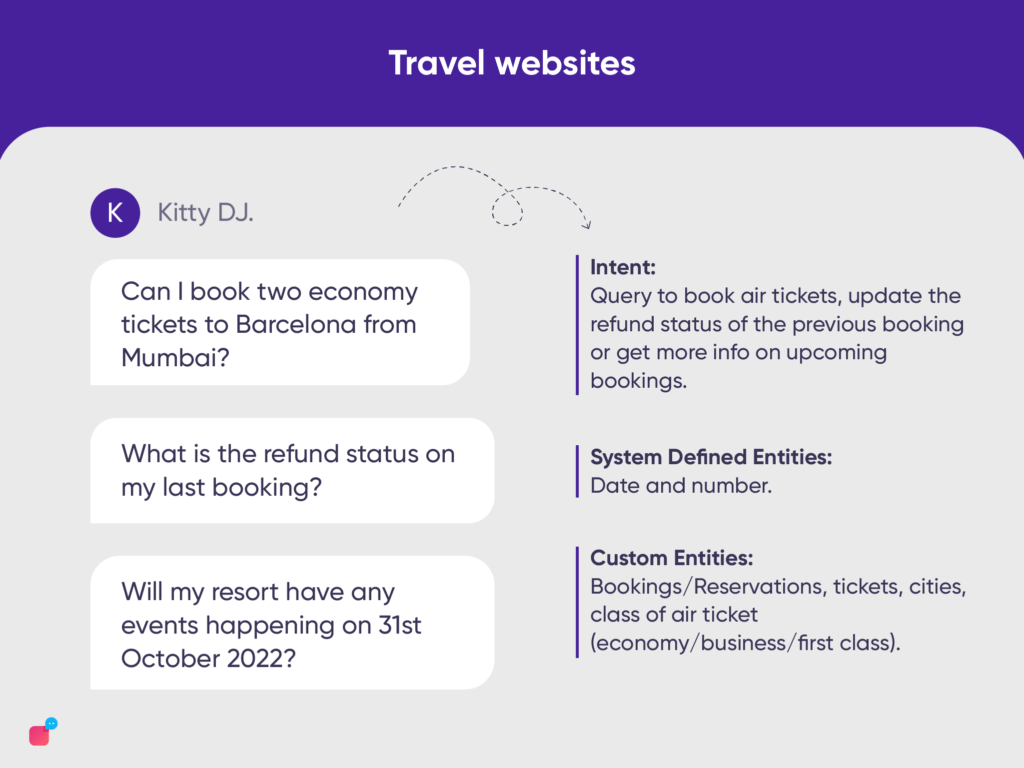
Some examples of chatbot intents and utterances initiated by customers can be:
“Can I book two economy tickets to Barcelona from Mumbai?”, “What is the refund status on my last booking?”, “Will my resort have any events happening on 31st October 2022?”
In the above user utterances, we can finally identify
- Intent: Query to book air tickets, update the refund status of the previous booking or get more info on upcoming bookings.
- System Defined Entities: Date and number.
- Custom Entities: Bookings/Reservations, tickets, cities, class of air ticket (economy/business/first class).
5. Generating marketing leads
The only way to meet customer expectations and demands is to truly understand them, break down the pain points that might be affecting them, and provide agile solutions. But how do chatbots help in this regard?
The presence of a chatbot helps by providing a smoother experience to a customer visiting a particular site for the first time. It can interact with the customer and provide swift responses, get a fair understanding of their requirements, answer FAQs and make them understand the functioning of a site. This entire transaction will ensure two things.
- The customer has received a positive experience on the site.
- A potential lead exists upon tracking down their requirements.
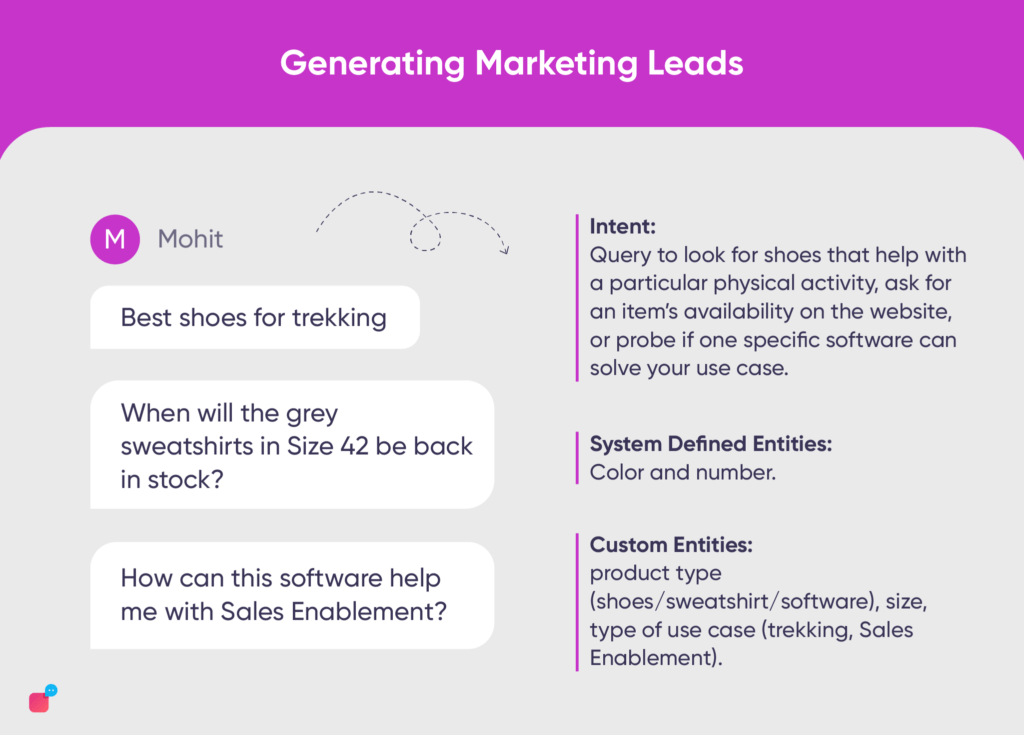
Suppose an online store installs a chatbot to understand its customer’s needs better. Some examples of chatbot intents and utterances initiated by customers can be:
“Best shoes for trekking.”, “When will the grey sweatshirts in Size 42 be back in stock?.”, “How can this software help me with Sales Enablement?”
In the above user utterances, we can finally identify
- Intent: Query to look for shoes that help with a particular physical activity, ask for an item’s availability on the website, or probe if one specific software can solve your use case.
- System Defined Entities: Color and number.
- Custom Entities: product type (shoes/sweatshirt/software), size, type of use case (trekking, Sales Enablement).
Build smarter chatbots with intents and entities
AI chatbots are taking up the world for their accuracy and natural conversations. The major NLP and Conversational AI advancements over a few years have enabled chatbots to perform significant transformations and satisfactory results in fields such as customer service and beyond.
Intents and entities are evidently a solid platform for substantial changes and improvements, right from training a chatbot to being mindful of a user’s needs and expectations or enabling a chatbot to cater to such conditions and expectations with accuracy and efficiency.
Verloop.io is the world’s leading provider of conversational AI for customer support. Our AI chatbots and voice bot solutions contain phenomenal intents and entities. Talk to our experts about what our solutions can do for your business.