AI agents are autonomous software entities designed to perform specific tasks and assist users across various domains with the help of internal and external knowledge bases. These agents leverage artificial intelligence techniques to understand natural language, reason, and take responsive actions. Here are some key principles that define AI agents:

1. Rational Decision-Making
AI agents make decisions based on their perceptions and data to optimise performance. For instance, an AI agent in a contact centre might ask questions, look up information, and respond to customer queries efficiently.
2. Sensing and Action
An AI agent senses its environment through physical or software interfaces. For example, a robotic agent gathers sensor data to navigate, while an AI Agent uses customer queries as input to provide appropriate responses.
3. Predictive Analysis
AI agents analyse collected data to predict outcomes that align with their goals. Self-driving cars, for instance, navigate obstacles and traffic conditions using data from multiple sensors to make real-time decisions.
AI agents operate through a combination of advanced technologies and methodologies, enabling them to perform tasks autonomously and interact effectively with humans. Here’s a technical overview of the key components that power AI agents:
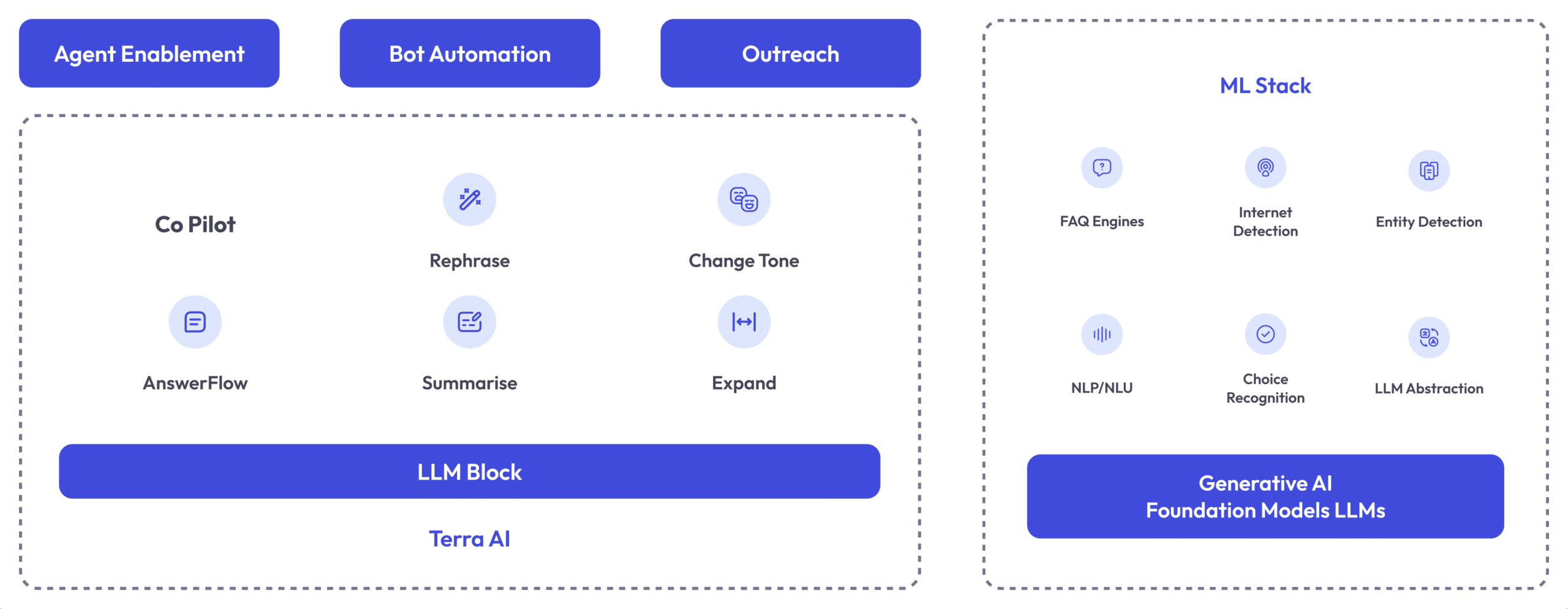
Natural Language Processing is a core technology that allows AI systems to engage with humans using natural language, facilitating fluid and intuitive interactions. NLP enables AI Agents to understand and generate human language, making conversations with AI agents feel more natural and effective.

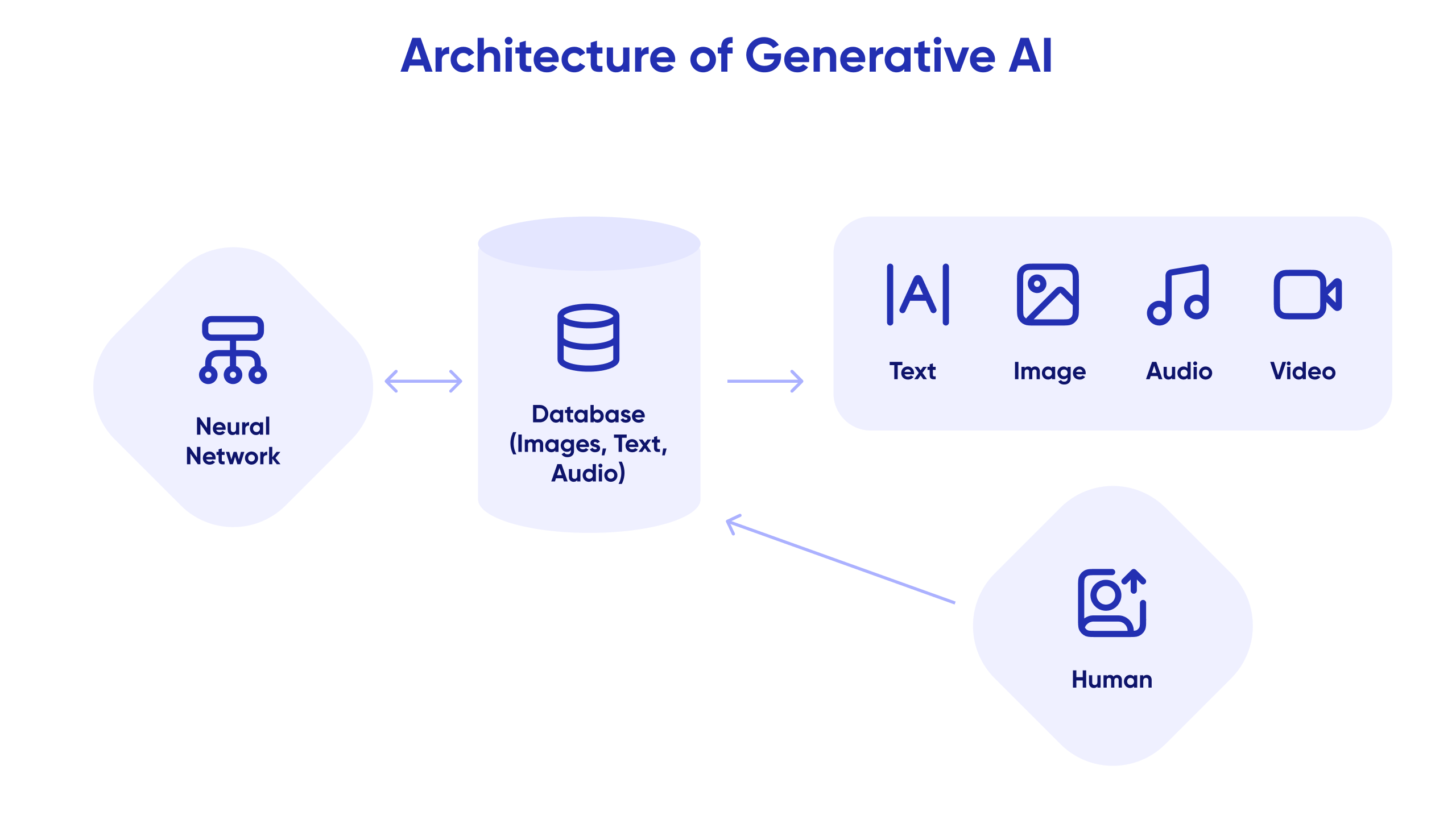
Machine Learning is a branch of AI that empowers machines to emulate intelligent human behaviour. By learning from data and experiences, AI agents can adapt and improve over time. This capability allows them to make more accurate predictions, enhance decision-making processes, and provide more personalised interactions.
Large Language Models refer to a tailored suite of algorithms designed specifically for tasks like those in contact centres. These models streamline processes and ensure efficient, high-quality automated customer service. They enable AI agents to deliver swift and effective responses, enhancing the overall customer experience.


Simple AI agents use predefined rules to make decisions. These systems follow a set of “if-then” rules to perform specific tasks, offering straightforward solutions for well-defined problems.
AI agents use knowledge representation to store and reason with information. This involves structuring data in a way that the AI can understand and manipulate to make informed decisions and give suitable responses.

Automated planning involves determining the optimal sequences of actions to achieve specific goals. AI agents use planning algorithms to map out steps and strategies, ensuring they can accomplish tasks efficiently and effectively.
By integrating these technologies and techniques, AI agents are able to operate autonomously, learn from interactions, and continuously improve their performance, offering sophisticated solutions and enhancing user experiences across various domains.
AI agents are invaluable assistants across various fields, continuously learning and adapting to provide smarter, more efficient support. Whether it’s answering queries, solving problems, or learning from experiences, these digital dynamos are always ready to lend a helping hand.

AI agents excel at responding to user queries or commands by executing predefined actions. Imagine an AI Agent in your university’s helpdesk that can provide real-time answers to student inquiries, like a digital concierge ready to assist at a moment’s notice. Whether it’s reminding you of your exam schedule or helping you navigate course selections, it’s like having a helpful assistant with encyclopaedic knowledge at your fingertips.
These clever agents don’t just parrot back information—they analyse context and make decisions based on the available data. Picture an AI tutor that can adjust its teaching methods based on a student’s progress. It can switch tactics if it detects that the student is struggling with a particular concept, much like a seasoned teacher who knows when to shift gears to keep the class engaged.


AI agents are the ultimate problem solvers, capable of tackling complex issues, optimising processes, and recommending solutions. Think of them as digital detectives, using their analytical prowess to piece together clues and solve mysteries. For instance, in logistics, an AI agent can streamline delivery routes, ensuring packages arrive faster and reducing fuel consumption—efficiency worthy of Sherlock Holmes himself.
These agents are not static; they learn from data and improve their performance over time. Thanks to machine learning algorithms, they adapt to new scenarios. A classic example is a recommendation system that gets better with use, like a personal shopper who knows your style inside out and always picks the perfect outfit.
After executing actions, AI agents don their analytical hats to assess the impact of their decisions and adjust strategies accordingly. It’s akin to a chess player reviewing past games to refine future tactics. For example, in customer service, an AI agent can analyse the success of different interaction strategies and fine-tune its approach to boost customer satisfaction.
The choice of agent type depends on the specific problem and context, as each type has its strengths and limitations. AI agents can be grouped into several classes based on their degree of perceived intelligence and capability. Understanding these different types helps in selecting the right AI agent for a given application. Here’s an expanded look at each type:
1. Simple Reflex AI Agents
These agents make decisions based solely on the current input without considering past experiences or future implications. They operate using predefined condition-action rules, often referred to as “if-then” statements.
2. Model-Based Reflex AI Agents
These agents maintain an internal model of the world that helps them make more informed decisions. They take into account both the current percept and the history of previous percepts to inform their actions.
3. Goal-Based AI Agents
These agents are designed to achieve specific goals, planning their actions accordingly. They consider the current state, the desired state, and the actions available to reach the desired state.
4. Utility-Based AI Agents
These agents evaluate actions based on utility or preference functions, aiming to maximise their expected utility. They choose actions that yield the highest utility according to their preferences.
5. Learning AI Agents
These agents improve over time by learning from their experiences and data. They adapt their behaviour based on feedback and new information.
6. Multi-Agent Systems
These systems involve multiple AI agents that interact with each other, which can include collaboration, competition, or negotiation. They work together to achieve individual or collective goals.
7. Hierarchical AI Agents
These agents have multiple layers of decision-making, with higher-level agents controlling lower-level ones. Each layer manages different aspects of a task, allowing for more complex and refined control.
By integrating AI agents across various industries, businesses can enhance efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction, proving that these digital wizards are worth their weight in gold.
In the world of finance, AI agents are like the unsung heroes of finance support. They can automate support with human-like conversation flows. For those needing financial advice, AI agents offer personalised recommendations, making them your very own digital financial advisor who never sleeps. It can also assist in obtaining transaction details, KYC and other financial support.


When it comes to transportation, AI agents are at the helm, quite literally. Autonomous vehicles rely on these agents for safe navigation, using real-time data to dodge traffic jams and avoid accidents as deftly as a London cabbie. Traffic management systems also benefit from AI agents coordinating traffic lights and signals to keep the urban flow as smooth as a well-oiled machine.
In the healthcare sector, AI agents are akin to having a team of experts on call 24/7. Drug discovery is expedited as AI agents process which compounds could lead to breakthrough medicines. Apart from this, AI agents can easily manage appointments, send reminders for medicine updates and more. Using AI agents, healthcare centres like clinics and hospitals can automate all their patient communication and management without any hassle.


AI agents in robotics are the brain behind the brawn. Industrial robots utilise AI for tasks requiring precision and efficiency, from assembling intricate electronics to welding car parts with pinpoint accuracy. Drones, too, benefit from AI agents, navigating through complex environments for tasks such as surveying construction sites or delivering packages, making them the ultimate multitaskers.
In the gaming world, AI agents are the clever opponents that keep players on their toes. These agents adapt to player behaviour, offering a dynamic and challenging experience that evolves as you play. Imagine playing chess against an opponent who learns from every move you make – that’s the power of AI in gaming, ensuring endless entertainment and new challenges.


AI agents are the vigilant guardians of the digital realm. They detect threats by analysing patterns and behaviours that might elude human analysts. With these agents at the helm, systems are protected against cyber-attacks, ensuring that your data stays safer than the Crown Jewels in the Tower of London.
In customer service, AI agents are the epitome of efficiency and personalisation. They can provide real-time support, resolving queries faster than you can say “customer satisfaction.” They personalise responses based on past interactions, making each customer feel valued and understood, much like having a personal butler for your digital needs.

By incorporating AI agents into your customer service strategy, you not only improve efficiency and satisfaction but also build a foundation of trust and personalisation that elevates the entire customer experience.
AI agents are diligent workers behind the scenes, handling routine inquiries with ease. By automating these repetitive tasks, human agents are freed up to tackle more complex and nuanced issues. This also impacts the response and resolution time, thus overall improving the customer experience. With the solution, 80% of the queries are easily resolved, leading to a decrease in the overall inbound call volume.

Through the magic of data analysis, AI agents can tailor interactions based on user preferences and history. This means each customer feels uniquely valued as if they have a personal assistant who knows their likes and dislikes. For example, an AI agent can recommend products or services based on previous purchases, making the customer experience more engaging and bespoke.
AI Agents are like having a customer service representative available 24/7. These solutions provide instant assistance, reducing response times significantly. Whether it’s the middle of the night or a busy holiday period, your customers receive timely support, enhancing their overall experience and satisfaction.


AI agents don’t just interact with customers—they also gather and analyse data to uncover valuable insights. By identifying trends, preferences, and pain points, these agents provide a clearer picture of customer behaviour. This information is crucial for making informed decisions that improve products, services, and customer interactions.
Streamlining processes with AI agents leads to faster issue resolution. By efficiently handling routine queries and managing customer interactions, these agents help improve overall CX. The result is a smoother, more efficient service that keeps customers happy and loyal. And as mentioned earlier, it significantly reduces the overall call volume that agents have to deal with without a conversation automation solution, thus bringing down support ops costs.


Transparent AI interactions are key to building trust with customers. When customers know they are interacting with an AI and see the benefits—like quick responses and personalised service—they are more likely to trust the system. Transparency in the way AI agents handle data and address issues is crucial in building trust and a dependable relationship between businesses and their customers.
The future of AI agents in business is brimming with potential. As these intelligent systems become more sophisticated, they are set to drive unprecedented levels of efficiency, innovation, and customer satisfaction. Organisations that embrace this transformative technology will be better positioned to stay competitive in an increasingly AI-driven marketplace.
AI agents are evolving beyond mere tools to become integral partners in delivering exceptional customer experiences. Their ability to handle dynamic and automated tasks with the help of internal and external knowledge bases will redefine business interactions, making every touchpoint smarter and more efficient. For instance, imagine AI agents that can not only predict customer needs before they arise but also offer bespoke solutions tailored to individual preferences—much like having a digital concierge at your service.